

接下来对视觉处理模块的代码seg_and_det.launch.py进行详解 代码如下:
def generate_launch_description():
## 返回启动描述列表,包含三个视觉处理节点
return LaunchDescription([
## 物体检测节点 - 负责识别和定位场景中的物体
Node(
package='vision', ## 所属功能包
executable='obj_detect', ## 可执行文件名
name='obj_detect', ## 节点名称
output='screen' ## 输出方式:打印到屏幕
),
## 检测坐标变换节点 - 负责计算检测到的物体相对于机器人基座的坐标变换
Node(
package='vision', ## 所属功能包
executable='det_tf', ## 可执行文件名
name='det_tf', ## 节点名称
output='screen' ## 输出方式:打印到屏幕
),
## 点云处理节点 - 负责处理深度相机获取的点云数据
Node(
package='vision', ## 所属功能包
executable='point_cloud_processor', ## 可执行文件名
name='point_cloud_processor', ## 节点名称
output='screen' ## 输出方式:打印到屏幕
)
])这个launch文件定义了三个视觉处理节点:
- obj_detect节点 - 负责物体检测功能,识别和定位场景中的物体
- det_tf节点 - 负责检测坐标变换,计算检测到的物体相对于机器人基座的坐标变换关系
- point_cloud_processor节点 - 负责点云处理,处理深度相机获取的点云数据 每个节点都来自vision功能包,并且都设置为将输出打印到屏幕,方便调试和监控。
obj_detect节点详解#
由上述代码可知,该节点是vision包下的obj_detect.py文件,内容如下:
class ObjDetect(Node):
"""
目标检测节点类
该类继承自ROS 2 Node类,实现基于YOLO模型的目标检测功能,
包括图像订阅、目标检测、深度估计、目标追踪和结果发布等功能。
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化目标检测节点
设置参数、加载模型、初始化订阅者和发布者等。
"""
super().__init__("obj_detect")
self.declare_parameter("model_path", "/home/whisper/ros2_ws/src/ros2_moveit2_ur5e_grasp/src/vision/vision/yolov11/models/best.pt")
self.declare_parameter("depth_topic", "/depth_registered/image_rect")
self.declare_parameter("image_topic", "/color/image_raw")
self.declare_parameter("cam_info_topic", "/color/camera_info")
self.declare_parameter("view_image", True)
self.declare_parameter("publish_result", True)
## 参数读取
model_path = self.get_parameter("model_path").value
self.view_img = self.get_parameter("view_image").value
self.publish_result = self.get_parameter("publish_result").value
## 模型加载
self.model = YOLO(model_path)
self.names = self.model.names
self.bridge = CvBridge()
self.tracker = Tracker()
self.depth_instrinsic_inv = np.eye(3)
self.depth = None
self.image = None
## ROS2 订阅与发布
self.create_subscription(Image, self.get_parameter("depth_topic").value, self.depth_callback, 10)
self.create_subscription(Image, self.get_parameter("image_topic").value, self.image_callback, 10)
self.create_subscription(CameraInfo, self.get_parameter("cam_info_topic").value, self.caminfo_callback, 10)
self.detection_pub = self.create_publisher(Detection2DArray, "/detection", 10)
self.image_pub = self.create_publisher(Image, "/detect_track", 10)
self.timer = self.create_timer(0.1, self.timer_callback)
self.get_logger().info("YOLOv11 ObjDetect Node Initialized.")
def caminfo_callback(self, msg):
"""
相机信息回调函数
获取相机内参矩阵并计算其逆矩阵,用于后续的深度估计和3D坐标计算。
Args:
msg (CameraInfo): 相机信息消息,包含相机内参矩阵K
"""
K = np.array(msg.k).reshape(3, 3)
self.depth_instrinsic_inv = np.linalg.inv(K)
def depth_callback(self, msg):
"""
深度图像回调函数
保存接收到的深度图像消息,供后续处理使用。
Args:
msg (Image): 深度图像消息
"""
self.depth = msg
def image_callback(self, msg):
"""
彩色图像回调函数
保存接收到的彩色图像消息,供后续处理使用。
Args:
msg (Image): 彩色图像消息
"""
self.image = msg
def timer_callback(self):
"""
定时器回调函数
定期执行目标检测、追踪和结果发布等核心功能。
"""
if self.depth is None or self.image is None:
return
## 获取图像
dep = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(self.depth, desired_encoding='passthrough')
img0 = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(self.image, desired_encoding='bgr8')
## 模型推理
results = self.model.predict(img0, verbose=False)
res = results[0]
boxes = res.boxes.xyxy.cpu().numpy()
confs = res.boxes.conf.cpu().numpy()
clses = res.boxes.cls.cpu().numpy()
## 目标追踪
detections = [[int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)] for x1, y1, x2, y2 in boxes]
tracks = self.tracker.update(detections)
## 构造 Detection2DArray
detection_result = Detection2DArray()
detections_list = []
for (x1, y1, x2, y2), conf, cls_id in zip(boxes, confs, clses):
cx, cy = int((x1 + x2) / 2), int((y1 + y2) / 2)
detection = Detection2D()
detection.id = self.names[int(cls_id)]
detection.bbox.center.position.x = float(cx)
detection.bbox.center.position.y = float(cy)
detection.bbox.size_x = float(x2 - x1)
detection.bbox.size_y = float(y2 - y1)
## 深度估计
Z = dep[cy, cx] * 1e-3
if Z <= 0 or np.isnan(Z): ## 防止无效的深度值
continue
uv1 = np.array([cx, cy, 1.0])
XYZ = self.depth_instrinsic_inv @ uv1 * Z
obj_hypothesis = ObjectHypothesisWithPose()
obj_hypothesis.hypothesis.class_id = self.names[int(cls_id)]
obj_hypothesis.hypothesis.score = float(conf)
obj_hypothesis.pose.pose.position.x = float(XYZ[0])
obj_hypothesis.pose.pose.position.y = float(XYZ[1])
obj_hypothesis.pose.pose.position.z = float(XYZ[2])
detection.results.append(obj_hypothesis)
detections_list.append(detection)
## 可视化
if self.view_img:
cv2.circle(img0, (cx, cy), 3, (0, 0, 255), -1)
## 按 x 坐标(从左到右)排序目标检测结果
sorted_detections = sorted(detections_list, key=lambda det: det.bbox.center.position.x)
detection_result.detections.extend(sorted_detections)
## 画 track ID
sorted_tracks = sorted(tracks, key=lambda track: track['bbox'][0])
for visual_idx, track in enumerate(sorted_tracks):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = track['bbox']
## 显示 ID(绿色)+ 排序编号(蓝色)
cv2.putText(img0, f"Rank {visual_idx+1}", (x1, y1 - 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 0, 0), 2)
## 画框
cv2.rectangle(img0, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
## 发布检测结果和追踪图像
if self.view_img:
image_msg = self.bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(img0, encoding='bgr8')
image_msg.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
self.image_pub.publish(image_msg)
if self.publish_result:
detection_result.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
self.detection_pub.publish(detection_result)
参数的设置与读取
self.declare_parameter("model_path", "/home/whisper/ros2_ws/src/ros2_moveit2_ur5e_grasp/src/vision/vision/yolov11/models/best.pt")
self.declare_parameter("depth_topic", "/depth_registered/image_rect")
self.declare_parameter("image_topic", "/color/image_raw")
self.declare_parameter("cam_info_topic", "/color/camera_info")
self.declare_parameter("view_image", True)
self.declare_parameter("publish_result", True)
## 参数读取
model_path = self.get_parameter("model_path").value
self.view_img = self.get_parameter("view_image").value
self.publish_result = self.get_parameter("publish_result").value这是一系列 self.declare_parameter(...) 调用,每个都为当前 ROS 2 节点声明一个可配置的参数。
语法:
self.declare_parameter(...)- name: 参数的名称(字符串)
- value: 参数的默认值。如果启动时没有通过外部方式指定该参数,就使用这个值
self.model = YOLO(model_path)- 从model_path加载 YOLO 目标检测模型
self.names = self.model.names- 获取模型能够识别的类别名称列表。例如:{0: ‘apple’, 1: ‘cup’, 2: ‘box’}。
self.bridge = CvBridge()- 创建一个 CvBridge 对象,用于在 ROS 图像消息 和 OpenCV 图像(NumPy 数组) 之间进行转换。
self.tracker = Tracker()- 创建一个目标跟踪器(Tracker) 对象。
self.depth_instrinsic_inv = np.eye(3)- 初始化一个 3x3 单位矩阵,用于存放相机内参的逆矩阵。
- 要将图像中的 2D 像素坐标 (u, v) 和深度值 d 转换为 3D 空间坐标 (x, y, z),需要使用相机内参矩阵 K,公式如下:
转换成矩阵形式:
self.create_subscription(Image, self.get_parameter("depth_topic").value, self.depth_callback, 10)
self.create_subscription(Image, self.get_parameter("image_topic").value, self.image_callback, 10)
self.create_subscription(CameraInfo, self.get_parameter("cam_info_topic").value, self.caminfo_callback, 10)
self.detection_pub = self.create_publisher(Detection2DArray, "/detection", 10)
self.image_pub = self.create_publisher(Image, "/detect_track", 10)这段代码是用于 ROS 2 节点初始化的一部分,主要负责订阅话题、发布话题。
例如self.create_subscription(Image, self.get_parameter("depth_topic").value, self.depth_callback, 10):
- 作用:创建一个订阅者,监听深度图像话题。
- 参数:
- Image:消息类型,表示接收到的是一个图像。
- self.get_parameter(“depth_topic”).value:从节点参数中获取深度图像的话题名称。
- self.depth_callback:当接收到新消息时调用的回调函数。
- 10:队列大小(QoS),限制未处理消息的最大数量。
在介绍话题发布者之前,需要先介绍self.timer = self.create_timer(0.1, self.timer_callback),因为通过这段代码不断调用self.timer_callback函数生成话题发布所需要的信息。这行代码的作用是:创建一个定时器(Timer),让它每隔 0.1 秒自动调用一次 self.timer_callback 函数。
接下来介绍self.timer_callback 函数:
def timer_callback(self):
"""
定时器回调函数
定期执行目标检测、追踪和结果发布等核心功能。
该函数是整个节点的核心处理逻辑,负责图像处理、目标检测、
三维位置计算、目标追踪和结果可视化等任务。
"""
## 检查是否有有效的深度图像和彩色图像数据
## 如果任一图像为空,则跳过本次处理
if self.depth is None or self.image is None:
return
## 获取图像数据
## 将ROS图像消息转换为OpenCV格式
## dep: 深度图像,保持原始编码格式
## img0: 彩色图像,转换为BGR8格式
dep = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(self.depth, desired_encoding='passthrough')
img0 = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(self.image, desired_encoding='bgr8')
## 使用YOLO模型进行目标检测推理
## verbose=False: 不输出详细日志信息
## results: 包含检测结果的列表
## res: 第一个(也是唯一一个)检测结果
## boxes: 检测到的目标边界框坐标 [x1, y1, x2, y2]
## confs: 每个检测结果的置信度分数
## clses: 每个检测结果的类别ID
results = self.model.predict(img0, verbose=False)
res = results[0]
boxes = res.boxes.xyxy.cpu().numpy()
confs = res.boxes.conf.cpu().numpy()
clses = res.boxes.cls.cpu().numpy()
## 目标追踪处理
## 将检测到的边界框坐标转换为整数格式
## 调用追踪器更新目标位置并获取追踪结果
detections = [[int(x1), int(y1), int(x2), int(y2)] for x1, y1, x2, y2 in boxes]
tracks = self.tracker.update(detections)
## 构造Detection2DArray消息,用于发布检测结果
## detection_result: 最终发布的检测结果数组
## detections_list: 临时存储检测结果的列表
detection_result = Detection2DArray()
detections_list = []
## 遍历所有检测到的目标
for (x1, y1, x2, y2), conf, cls_id in zip(boxes, confs, clses):
## 计算边界框中心点坐标
cx, cy = int((x1 + x2) / 2), int((y1 + y2) / 2)
## 创建Detection2D对象并设置基本属性
detection = Detection2D()
detection.id = self.names[int(cls_id)] ## 设置目标类别名称
## 设置边界框中心点坐标
detection.bbox.center.position.x = float(cx)
detection.bbox.center.position.y = float(cy)
## 设置边界框尺寸
detection.bbox.size_x = float(x2 - x1)
detection.bbox.size_y = float(y2 - y1)
## 深度估计和3D位置计算
## 从深度图像中获取中心点的深度值并转换为米
Z = dep[cy, cx] * 1e-3
## 检查深度值是否有效(大于0且非NaN)
if Z <= 0 or np.isnan(Z): ## 防止无效的深度值
continue
## 构造齐次坐标 [cx, cy, 1]
uv1 = np.array([cx, cy, 1.0])
## 使用相机内参逆矩阵和深度值计算3D坐标
## XYZ = K^(-1) * [u, v, 1]^T * Z
XYZ = self.depth_instrinsic_inv @ uv1 * Z
## 创建目标假设对象并设置属性
obj_hypothesis = ObjectHypothesisWithPose()
obj_hypothesis.hypothesis.class_id = self.names[int(cls_id)] ## 设置类别ID
obj_hypothesis.hypothesis.score = float(conf) ## 设置置信度分数
## 设置3D位置坐标
obj_hypothesis.pose.pose.position.x = float(XYZ[0])
obj_hypothesis.pose.pose.position.y = float(XYZ[1])
obj_hypothesis.pose.pose.position.z = float(XYZ[2])
## 将目标假设添加到检测结果中
detection.results.append(obj_hypothesis)
## 将处理后的检测结果添加到列表中
detections_list.append(detection)
## 可视化处理:在图像上绘制中心点
if self.view_img:
## 在目标中心点绘制红色圆点
cv2.circle(img0, (cx, cy), 3, (0, 0, 255), -1)
## 按 x 坐标(从左到右)排序目标检测结果
## 便于机器人按顺序抓取目标
sorted_detections = sorted(detections_list, key=lambda det: det.bbox.center.position.x)
detection_result.detections.extend(sorted_detections)
## 对追踪结果按边界框的x坐标排序
## 保证追踪ID与检测结果的顺序一致
sorted_tracks = sorted(tracks, key=lambda track: track['bbox'][0])
## 在图像上绘制追踪结果
for visual_idx, track in enumerate(sorted_tracks):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = track['bbox']
## 显示排序编号(蓝色),位置在边界框上方
cv2.putText(img0, f"Rank {visual_idx+1}", (x1, y1 - 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (255, 0, 0), 2)
## 绘制绿色边界框
cv2.rectangle(img0, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
## 发布检测结果和追踪图像
## 如果启用了图像可视化,则发布处理后的图像
if self.view_img:
## 将OpenCV图像转换回ROS图像消息
image_msg = self.bridge.cv2_to_imgmsg(img0, encoding='bgr8')
## 设置消息时间戳为当前时间
image_msg.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
## 发布图像消息
self.image_pub.publish(image_msg)
## 如果启用了结果发布,则发布检测结果
if self.publish_result:
## 设置检测结果数组的时间戳
detection_result.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
## 发布检测结果
self.detection_pub.publish(detection_result)这个函数是整个目标检测节点的核心处理逻辑,主要功能包括:
-
数据检查:
- 检查深度图像和彩色图像是否有效
-
图像处理:
- 使用CvBridge将ROS图像消息转换为OpenCV格式 分别处理深度图像和彩色图像
-
目标检测:
- 使用YOLO模型对彩色图像进行推理 提取检测结果中的边界框、置信度和类别信息
-
目标追踪:
- 将检测结果传递给追踪器进行目标跟踪
- 获取追踪结果
-
三维位置计算:
- 从深度图像中获取目标中心点的深度值
- 结合相机内参逆矩阵计算目标的3D坐标
-
结果排序:
- 按照x坐标对检测结果进行排序,便于机器人按顺序抓取
-
可视化处理:
- 在图像上绘制检测中心点和追踪边界框
- 添加排序编号标识
-
结果发布:
- 发布处理后的可视化图像
- 发布目标检测和三维位置信息
经过上述代码处理之后的结果如下:
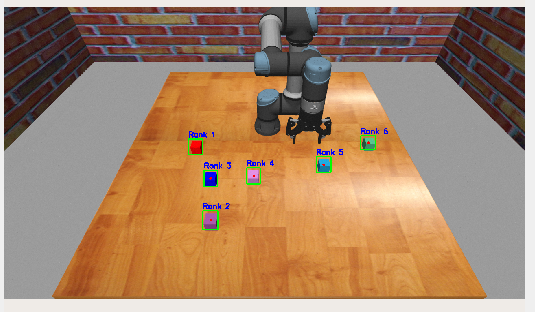 接下来介绍发布话题
接下来介绍发布话题
self.detection_pub = self.create_publisher(Detection2DArray, "/detection", 10)- 创建一个发布者(Publisher),用于将目标检测的结果(如物体类别、边界框、置信度等)发布到名为 /detection 的话题上。## det_tf节点详解
self.image_pub = self.create_publisher(Image, "/detect_track", 10)- 创建一个发布者,用于将带有检测的图像发布到 /detect_track 话题上。
det_tf节点详解#
代码内容如下:
class DetTF(Node):
"""
检测结果TF变换发布节点类
该类继承自ROS 2 Node类,负责订阅目标检测结果,
并将检测到的目标位置发布为TF变换,便于机器人系统
进行坐标变换和路径规划。
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化检测结果TF变换发布节点
创建目标检测结果订阅者和TF广播器。
"""
super().__init__('det_tf')
## 创建目标检测结果订阅者
self.subscription = self.create_subscription(
Detection2DArray, ## 消息类型:二维检测结果数组
'detection', ## 订阅话题名称
self.det_callback, ## 回调函数
10) ## 队列大小
self.subscription ## prevent unused variable warning
## 创建TF广播器,用于发布坐标变换
self.tf_broadcaster = TransformBroadcaster(self)
def det_callback(self, msg: Detection2DArray):
"""
目标检测结果回调函数
处理接收到的目标检测结果,提取特定类别的目标位置信息,
并按指定规则排序后发布为TF变换。
Args:
msg (Detection2DArray): 包含检测结果的消息
"""
## 定义要处理的目标类别名称
cls_name = 'cube'
## 存储检测到的目标位置信息
objs = []
## 遍历所有检测结果,筛选出指定类别的目标
for det in msg.detections:
if det.id == cls_name:
## 提取目标的3D位置信息
pos = det.results[0].pose.pose.position
objs.append(pos)
## 按照 x 坐标升序排序(从左到右)
objs.sort(key=lambda p: p.x)
## 广播 TF,按排序后的位置命名
for idx, pos in enumerate(objs, start=1):
## 创建坐标变换消息
t = TransformStamped()
## 设置时间戳为当前时间
t.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
## 设置父坐标系
t.header.frame_id = 'camera_color_optical_frame'
## 设置子坐标系,按顺序命名
t.child_frame_id = f'cube{idx}'
## 设置平移变换
t.transform.translation.x = pos.x
t.transform.translation.y = pos.y
t.transform.translation.z = pos.z
## 设置旋转变换(单位四元数,表示无旋转)
t.transform.rotation.w = 1.0
t.transform.rotation.x = 0.0
t.transform.rotation.y = 0.0
t.transform.rotation.z = 0.0
## 发布坐标变换
self.tf_broadcaster.sendTransform(t)
def main(args=None):
"""
主函数
初始化ROS 2节点并启动检测结果TF变换发布功能。
Args:
args: 程序启动参数
"""
## 初始化ROS 2客户端库
rclpy.init(args=args)
## 创建DetTF节点实例
det_tf = DetTF()
try:
## 循环处理节点消息
rclpy.spin(det_tf)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
## 处理键盘中断(Ctrl+C)
pass
## 销毁节点并关闭ROS 2客户端库
det_tf.destroy_node()
rclpy.shutdown()self.subscription = self.create_subscription(
Detection2DArray, ## 消息类型:二维检测结果数组
'detection', ## 订阅话题名称
self.det_callback, ## 回调函数
10 ## 队列大小
)- 创建一个订阅者(Subscriber),订阅话题detection,用于接收来自其他节点发布的 2D 目标检测结果。
self.subscription ## prevent unused variable warning- 防止代码分析工具或编译器报 “未使用变量” 警告。
- 在 Python 中,如果你只是把 create_subscription 的返回值赋给一个变量但没有读取或使用它,某些 Linter(如 pylint)会认为这是一个“未使用变量”,并发出警告。
- 实际上,你必须保存这个订阅者对象,否则它会被 Python 的垃圾回收机制销毁,导致订阅失败。
- 所以这行代码只是“读取”了一下 self.subscription,告诉工具:“我确实用了这个变量”,从而消除警告。
self.tf_broadcaster = TransformBroadcaster(self)- 创建一个 TF2 广播器(Transform Broadcaster),用于向 ROS 2 的 TF 树(Transform Tree) 发布坐标变换。
- 这个操作就可以是Base_link或Rviz知道这个物体的相对自己的具体位置
接下来介绍逻辑处理函数det_callback:
def det_callback(self, msg: Detection2DArray):
"""
目标检测结果回调函数
处理接收到的目标检测结果,提取特定类别的目标位置信息,
并按指定规则排序后发布为TF变换。
Args:
msg (Detection2DArray): 包含检测结果的消息
"""
## 定义要处理的目标类别名称
cls_name = 'cube'
## 存储检测到的目标位置信息
objs = []
## 遍历所有检测结果,筛选出指定类别的目标
for det in msg.detections:
if det.id == cls_name:
## 提取目标的3D位置信息
pos = det.results[0].pose.pose.position
objs.append(pos)
## 按照 x 坐标升序排序(从左到右)
objs.sort(key=lambda p: p.x)
## 广播 TF,按排序后的位置命名
for idx, pos in enumerate(objs, start=1):
## 创建坐标变换消息
t = TransformStamped()
## 设置时间戳为当前时间
t.header.stamp = self.get_clock().now().to_msg()
## 设置父坐标系
t.header.frame_id = 'camera_color_optical_frame'
## 设置子坐标系,按顺序命名
t.child_frame_id = f'cube{idx}'
## 设置平移变换
t.transform.translation.x = pos.x
t.transform.translation.y = pos.y
t.transform.translation.z = pos.z
## 设置旋转变换(单位四元数,表示无旋转)
t.transform.rotation.w = 1.0
t.transform.rotation.x = 0.0
t.transform.rotation.y = 0.0
t.transform.rotation.z = 0.0
## 发布坐标变换
self.tf_broadcaster.sendTransform(t)将目标检测的结果位置信息发布为TF变换,值得注意的是这些Cube的位置信息是相对于camera_color_optical_frame 坐标系的。
工作流程如下:
接收到 Detection2DArray 消息
↓
筛选出类别为 'cube' 的检测结果
↓
提取每个 cube 的 3D 位置 (x, y, z)
↓
按 x 坐标从小到大排序(从左到右)
↓
为每个 cube 创建一个 TF 坐标系:cube1, cube2, ...
↓
广播这些坐标系相对于相机的变换point_cloud_processor节点详解#
对于这个代码,我目前感觉对我们的这个项目没有什么用(可能看的还不够深入,不知道在哪里使用了),但是还是要解释一下,代码如下:
class PointCloudProcessor(Node):
"""
点云处理器节点类
该类继承自ROS 2 Node类,负责订阅原始点云数据,
根据指定参数对点云进行过滤处理,并发布过滤后的点云数据。
主要用于减少点云数据量,提高处理效率。
"""
def __init__(self):
"""
初始化点云处理器节点
声明参数、创建点云订阅者和发布者。
"""
super().__init__('point_cloud_processor')
## 声明参数
self.declare_parameter('proportion', 0.3) ## 点云保留比例,默认保留30%
self.declare_parameter('start_from_top', True) ## 是否从顶部开始截取点云,默认为True
## 创建点云订阅者,订阅原始点云数据
self.subscription = self.create_subscription(
PointCloud2, ## 消息类型:点云2
'/depth/points', ## 订阅话题名称
self.listener_callback, ## 回调函数
10) ## 队列大小
self.subscription ## prevent unused variable warning
## 创建点云发布者,发布过滤后的点云数据
self.publisher_ = self.create_publisher(PointCloud2, '/depth/points_filtered', 10)
def listener_callback(self, msg):
"""
点云数据回调函数
处理接收到的点云数据,根据参数设置过滤点云,
并发布过滤后的点云数据。
Args:
msg (PointCloud2): 接收到的原始点云数据消息
"""
## 获取参数值
proportion = self.get_parameter('proportion').value ## 点云保留比例
start_from_top = self.get_parameter('start_from_top').value ## 是否从顶部开始截取
## 处理有组织的点云(高度大于1)
if msg.height > 1: ## 有组织的点云
max_height = msg.height ## 原始点云高度
new_height = int(proportion * max_height) ## 计算新高度
## 检查新高度是否有效
if new_height < 1:
self.get_logger().info('New height too small, not publishing')
return
## 计算截取起始位置
if start_from_top:
## 从顶部开始截取
start = 0
else:
## 从底部开始截取
start = (msg.height - new_height) * msg.row_step
## 计算截取数据大小
data_size = new_height * msg.row_step
## 截取点云数据
new_data = msg.data[start : start + data_size]
## 创建新的 PointCloud2 消息
new_msg = PointCloud2()
new_msg.header = msg.header ## 复用原始消息的头部信息
new_msg.height = new_height ## 设置新高度
new_msg.width = msg.width ## 保持宽度不变
new_msg.fields = msg.fields ## 复用原始字段定义
new_msg.is_bigendian = msg.is_bigendian ## 复用字节序设置
new_msg.point_step = msg.point_step ## 复用点步长
new_msg.row_step = msg.row_step ## 复用行步长
new_msg.data = new_data ## 设置新数据
new_msg.is_dense = msg.is_dense ## 复用密集性标志
## 发布过滤后的点云
self.publisher_.publish(new_msg)
## 处理无组织的点云(高度为1)
elif msg.height == 1: ## 无组织的点云
max_width = msg.width ## 原始点云宽度
new_width = int(proportion * max_width) ## 计算新宽度
## 检查新宽度是否有效
if new_width < 1:
self.get_logger().info('New width too small, not publishing')
return
## 计算截取起始位置
if start_from_top:
## 从开始位置截取
start = 0
else:
## 从末尾开始截取
start = (msg.width - new_width) * msg.point_step
## 计算截取数据大小
data_size = new_width * msg.point_step
## 截取点云数据
new_data = msg.data[start : start + data_size]
## 创建新的 PointCloud2 消息
new_msg = PointCloud2()
new_msg.header = msg.header ## 复用原始消息的头部信息
new_msg.height = 1 ## 保持高度为1
new_msg.width = new_width ## 设置新宽度
new_msg.fields = msg.fields ## 复用原始字段定义
new_msg.is_bigendian = msg.is_bigendian ## 复用字节序设置
new_msg.point_step = msg.point_step ## 复用点步长
new_msg.row_step = new_width * msg.point_step ## 计算并设置行步长
new_msg.data = new_data ## 设置新数据
new_msg.is_dense = msg.is_dense ## 复用密集性标志
## 发布过滤后的点云
self.publisher_.publish(new_msg)
## 处理异常情况
else:
## 点云高度小于1,无法处理
self.get_logger().warn('Point cloud has height <1, cannot process')
这个文件实现了一个ROS 2节点,主要功能是对点云数据进行过滤处理。详细说明如下:
-
PointCloudProcessor类:
- 继承自ROS 2 Node类,实现点云处理功能
- 初始化时声明参数、创建点云订阅者和发布者
-
初始化方法:
- 声明两个参数:proportion(点云保留比例,默认0.3)和start_from_top(是否从顶部开始截取,默认True)
- 创建对/depth/points话题的订阅者,用于接收原始点云数据
- 创建对/depth/points_filtered话题的发布者,用于发布过滤后的点云数据
-
点云处理逻辑:
- listener_callback:处理接收到的点云数据
- 根据点云的组织形式(有组织或无组织)分别处理:
- 有组织点云(height > 1):按行进行截取,保持宽度不变,调整高度
- 无组织点云(height = 1):按点进行截取,调整宽度
- 根据start_from_top参数决定是从起始位置还是末尾位置开始截取
- 根据proportion参数确定截取的比例
-
点云数据处理:
- 计算新的点云尺寸(高度或宽度)
- 计算截取的起始位置和数据大小
- 从原始点云数据中截取相应部分
- 构建新的PointCloud2消息并发布
原始点云数据效果:

过滤后的点云效果:

总结#
这些节点共同构成了机器人视觉系统的核心部分,用于实现物体识别、定位和三维点云处理等功能,为后续的抓取规划提供必要的环境感知信息。
到此,我们的抓取的准备工作已经完成,也就是simulation.launch.py代码执行结束,接下来将执行start_grasp.launch.py代码。